Dual Boot Linux (Ubuntu 22.04) and Windows 11 on Modern Systems – UEFI
Thursday, December 7th, 2023Dual Boot Linux (Ubuntu 22.04) and Windows 11 on Modern Systems – UEFI
In order to setup a dual boot of Windows 11 and Ubuntu 22.04 on a modern system that uses UEFI, follow these steps.
- Install Windows 11 first leaving some unpartitioned space (at least 60GB is my recommendation) on the drive you're installing Windows on.
- Boot up the Ubuntu installer.
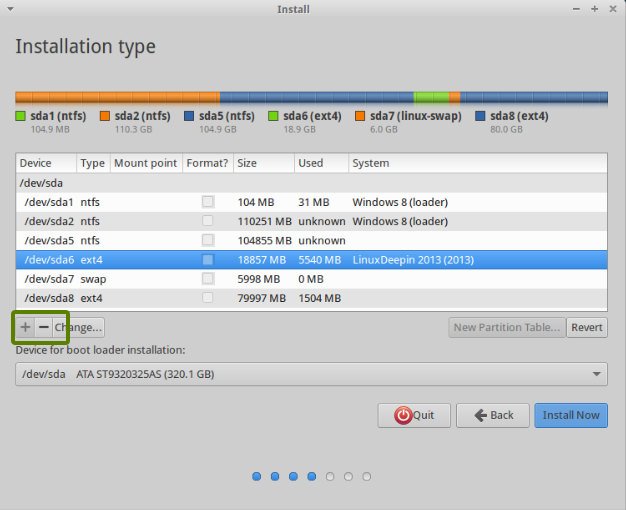
- During installation, you'll be presented with an Installation Type options screen. Choose "Something else".
- On the next screen, you'll see a list of drives and partitions. On the same drive you installed Windows, create 3 new partitions.
- Create an EXT4 partition for the / mount point at least 40GB in size (this is the main drive for Linux files).
- Create a SWAP partition at least 18GB in size.
- Create an EFI partition at least 500MB in size. This is extremely important in order to get grub to install properly.
- Leave the "Device for boot loader installation" set as the top level drive that Windows and Ubuntu was / is being installed on. You should not select an individual partition here.
- Complete the installation process.
- You might need to change the UEFI boot order in the BIOS of your system to boot Ubuntu / Linux first versus booting the Windows EFI partition. Since you created an EFI partition for your Linux install, it should show up as a bootable option in the bios. Set / adjust accordingly.
- That's it!